Physical architecture comparison
The following architectures were both designed with:
- A small/medium gas utility in mind
- Support for workflows with a target design load as described in the test methods section
- Consideration for key design choices
- AWS cloud infrastructure
The SAP HANA Private Cloud Edition (PCE) deployment mirrors the instance types and sizes but includes a separate VPC connected to the ArcGIS Enterprise VPC via AWS PrivateLink where the enterprise geodatabase is configured. EC2 and database instance types are identical between the two deployments, the key difference is the geodatabase hosting approach and network design.
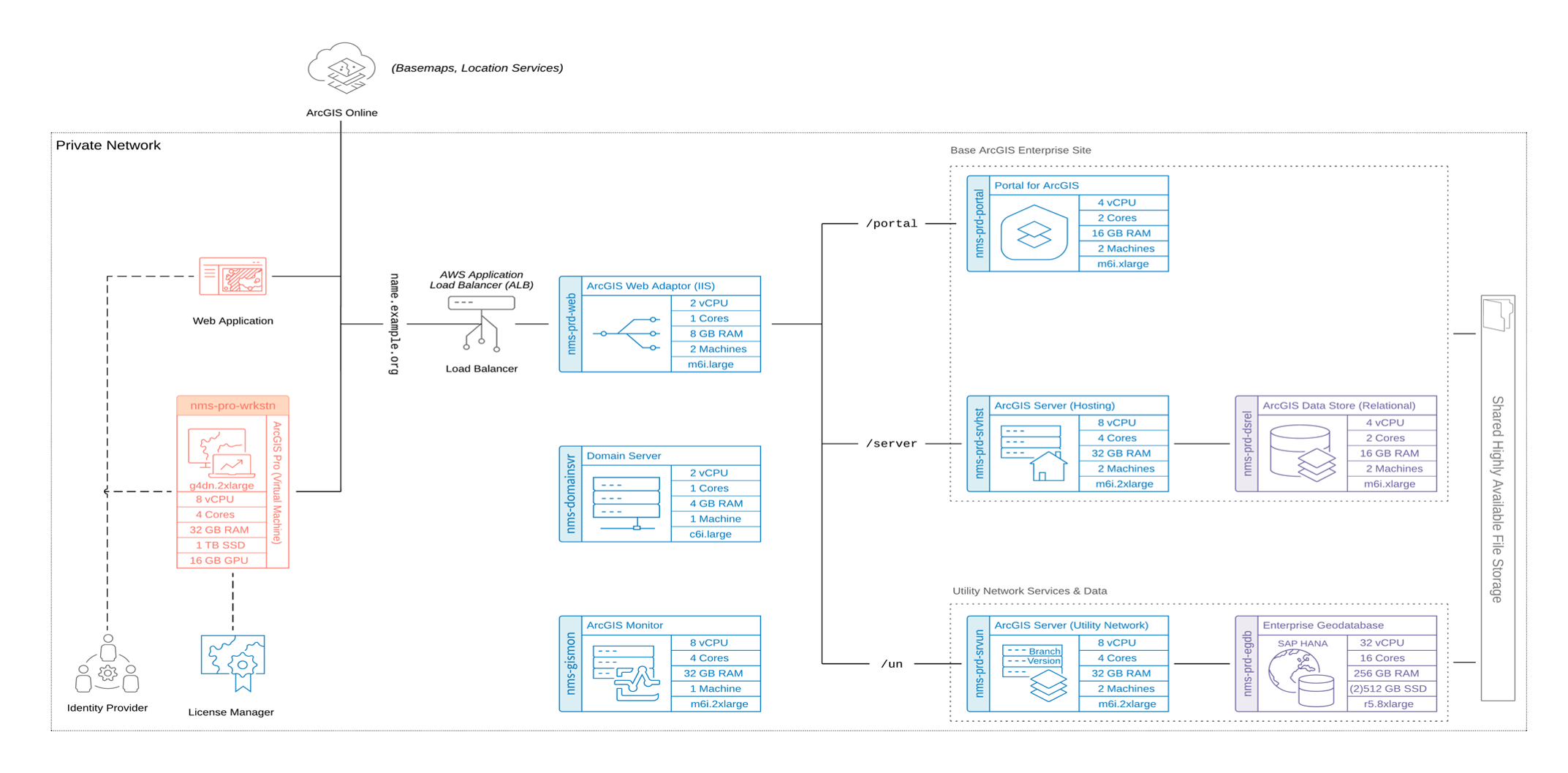
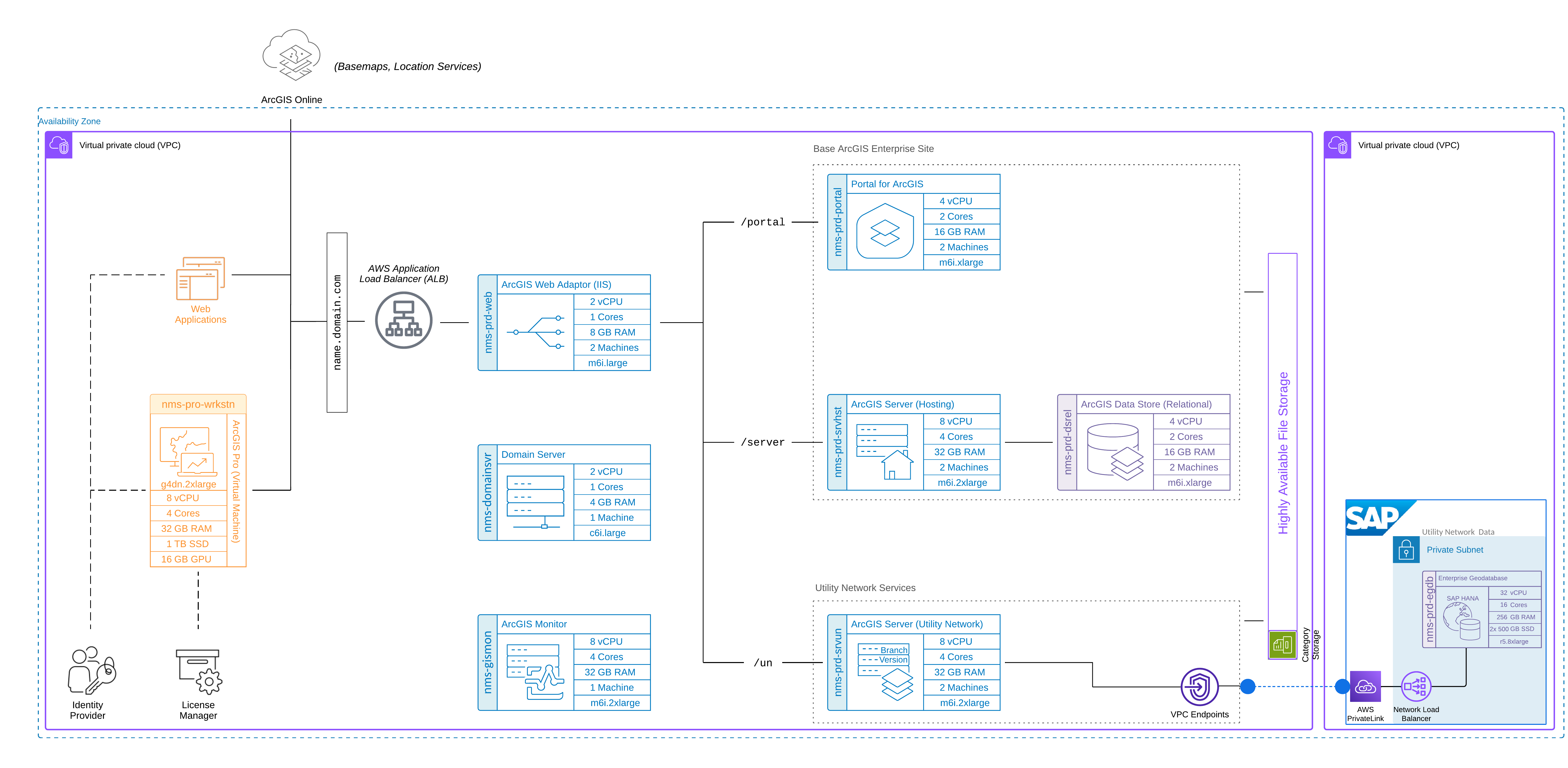
Instance types and configurations
The following system profiles detail the instance types that were chosen and validated for the scope and purpose of this test study. Both systems used the same number and type of AWS EC2 instances. For your own system design, it is highly recommended to follow a complete design process to account for your organization’s specific business and technical requirements.
Esri offers system architecture design services should you need help determining all the different factors relating to your organization’s physical design, such as networking, storage, system environments, and sizing. Minimum system requirements for each component are listed in the respective software documentation available online.
Desktop (ArcGIS Pro and browser-based workflows)
- 3 machines
- G4dn.2xlarge instance type
- 4 CPU (8 vCPU)
- 32 GB RAM
- 1 TB Disk
- 16 GB GPU
Portal for ArcGIS
- 2 machines
- M6i.xlarge instance type
- 2 CPU (4 vCPU)
- 16 GB RAM
- 128 GB Disk
ArcGIS GIS Server (Network Management services)
- 2 machines
- M6i.2xlarge instance type
- 4 CPU (8 vCPU)
- 32 GB RAM
- 128 GB Disk
ArcGIS GIS Server (hosting server)
- 2 machines
- M6i.2xlarge instance type
- 4 CPU (8 vCPU)
- 32 GB RAM
- 128 GB Disk
ArcGIS Data Store (relational)
- 2 machines
- M6i.xlarge instance type
- 2 CPU (4 vCPU)
- 16 GB RAM
- 256 GB Disk
ArcGIS Web Adaptor
- 2 machines
- M6i.large instance type
- 1 CPU (2 vCPU)
- 8 GB RAM
- 128 GB Disk
ArcGIS Monitor
- 1 machine
- M6i.2xlarge instance type
- 4 CPU (8 vCPU)
- 32 GB RAM
- 128 GB Disk
Shared file storage
- 1 instance
- C6i.xlarge
- 1 CPU (2vCPU)
- 8 GB RAM
- 2 TB Disk
Database host
- 1 machine
- R5.8xlarge instance type
- 16 CPU (32 vCPU)
- 256 GB RAM
- (2) 512 GB Disks
Domain server
- 1 machine
- C6i.large instance type
- 1 CPU (2vCPU)
- 4 GB RAM
- 128 GB Disk
Additional infrastructure considerations
The following are additional areas of consideration when designing a Network Information Management System and an explanation of some infrastructure choices made for this test study.
Application load balancer (ALB)
A load balancer is required in a highly available ArcGIS Enterprise deployment to balance and proxy client traffic to the portal and server components as well as intra-site traffic between the software components. Although the ArcGIS Web Adaptor operates as a load balancer, it is insufficient on its own to serve as a load balancer in a high availability configuration. In this test study, an AWS Application Load Balancer was used.
Shared storage
To successfully implement a highly available ArcGIS Enterprise deployment, several configuration items or folders must be stored in a highly available, shared location. This ensures the data remains accessible even if one server fails, providing uninterrupted service to end-users. Additionally, shared storage simplifies data management in a multi-machine deployment and improves scalability by centralizing data storage and allowing for expansion as needed. In this architecture, a Windows-based file server is used to store these shared components, which is configured with AWS EC2 automatic recovery.
System components not included in the diagram
Not illustrated in the architecture diagram are antivirus software and AWS networking components that were present and active during the test study.