ArcGIS Enterprise on Kubernetes (software)
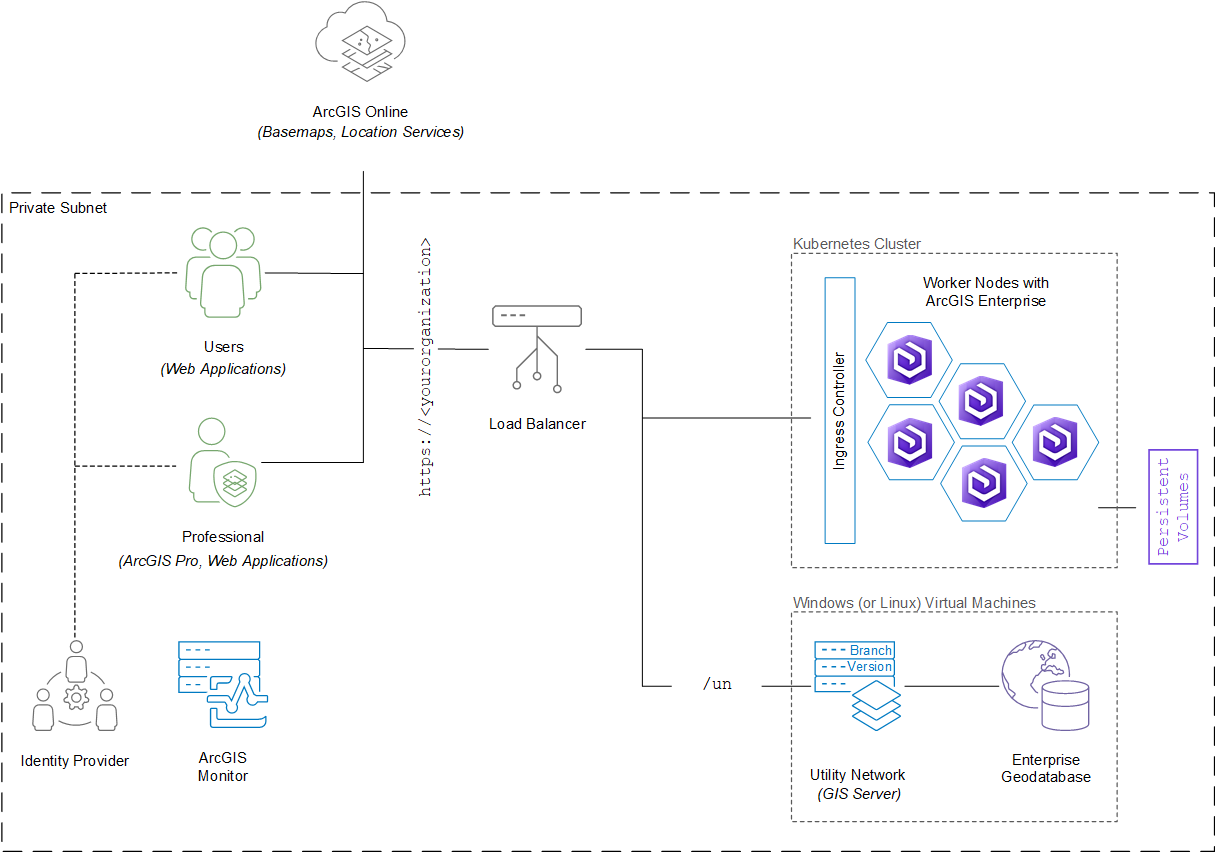
This logical view of the reference architecture supports all implementation options of the network information management system and defines individual software components, how they are separated or combined, and key interactions between them.
Download a Microsoft Visio file of this logical architecture.
Learn more about diagramming resources for ArcGIS systems.
Note:
This reference architecture was designed with a focus on specific workflows and capabilities.
Software components
The diagram above contains a variety of software components that contribute to the overall system design, including:
- Applications provide end-users with access to system capabilities. The primary applications used in a network information management system are:
- ArcGIS Pro - a professional GIS desktop application used by editors
- Configurable applications and application builders used by general users and editors
-
An ArcGIS Enterprise on Kubernetes deployment
-
An additional federated ArcGIS Server (Windows or Linux) site that is federated with the ArcGIS Enterprise on Kubernetes deployment. This server must support ArcGIS Utility Network editing services. This is required for implementation options 2 and 3.
- This federated server site can be at a prior supported version, provided it meets the network management release plan and is not also designated as a Raster Analytics or Image hosting site.
-
An enterprise geodatabase for storing and managing an ArcGIS Utility Network through a supported relational database management system (DBMS). This is required for implementation options 2 and 3.
-
Load balancing and reverse proxy capabilities are provided by a load balancer.
-
An identity provider is recommended for single sign-on (SSO) within the enterprise, though not strictly required. Learn more about ArcGIS authentication models and providers.
-
ArcGIS Monitor for monitoring and optimizing the federated ArcGIS Server site supporting ArcGIS Utility Network editing services.
- ArcGIS Online provides basemaps and other location services.
Product lifecyle
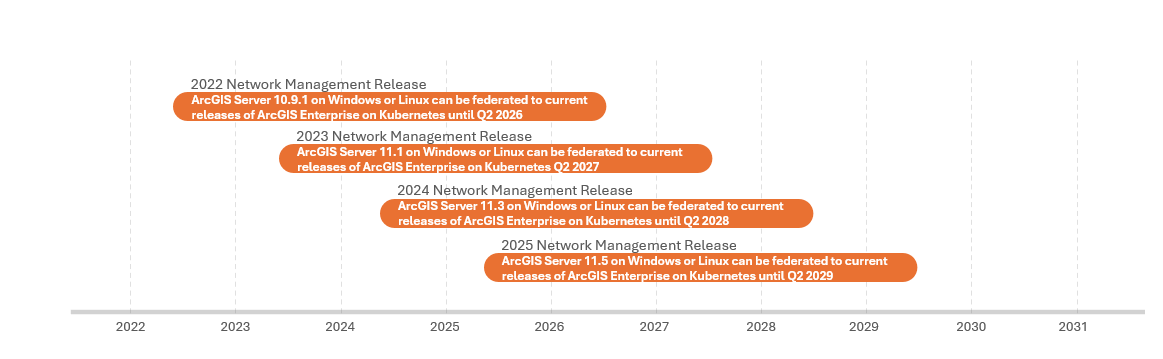
The ArcGIS Enterprise on Kubernetes product lifecyle differs and is separate from that of ArcGIS Enterprise on Windows and Linux.
Note:
Due to the ArcGIS Enterprise on Kubernetes life cycle, it is important to keep the additional federated ArcGIS Server site on a version supported by the network management release plan, and that the version of ArcGIS Enterprise on Kubernetes supports the federated ArcGIS Server site version.
The ArcGIS Network Management release plan designates specific long-term support releases of ArcGIS Enterprise and ArcGIS Pro as network management releases. Being on a network management release ensures regular patches for both ArcGIS Enterprise (4 years) and ArcGIS Pro (2 years per supported version) directly related to ArcGIS Utility Network workflows.
Key interactions
The software components described above interact with each other in the following ways:
-
Client applications communicate with enterprise data services over HTTPS, typically via stateless REST APIs. A friendly, well-defined domain name is recommended as the entry point to the system. Three separate ArcGIS Web Adaptor instances configured in the web server handle context path-based routing to the Portal for ArcGIS and ArcGIS Server components described above. Learn more about DNS, naming, and URLs.
-
Client applications communicate with basemaps, and location services provided by ArcGIS Online over HTTPS, typically via stateless REST APIs. This requires connectivity from client machines to the Internet.
-
ArcGIS Server maintains persistent TCP connections to both the database management system (DBMS) hosting the enterprise geodatabase as well as the ArcGIS Data Store. The former requires that appropriate database client software be installed on the ArcGIS Server machines communicating with the DBMS.
-
ArcGIS Monitor communicates with a variety of ArcGIS and IT (e.g., DBMS) components using a variety of mechanisms. See ArcGIS Monitor for more information.
-
References to location services hosted and managed by ArcGIS Online are typically registered and made available for use within ArcGIS Enterprise. See configuring ArcGIS Online utility services, configuring ArcGIS Living Atlas content, and distributed collaboration.
Related resources
- Learn more about ArcGIS Enterprise on Kubernetes.
- Learn more about data editing and management delivered through a Kubernetes based deployment pattern.